How Lean Principles Transform Manufacturing Workflows
Manufacturing businesses constantly seek ways to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and boost productivity. One of the most effective approaches is implementing lean principles. By focusing on eliminating waste and streamlining processes, manufacturers can achieve significant gains in operational performance and customer satisfaction.
Key Takeaways:
- Lean principles drastically reduce waste in manufacturing processes.
- Implementing lean principles leads to increased efficiency and productivity.
- A focus on continuous improvement is crucial for successful lean implementation.
- Value stream mapping and other lean tools are essential for identifying and eliminating bottlenecks.
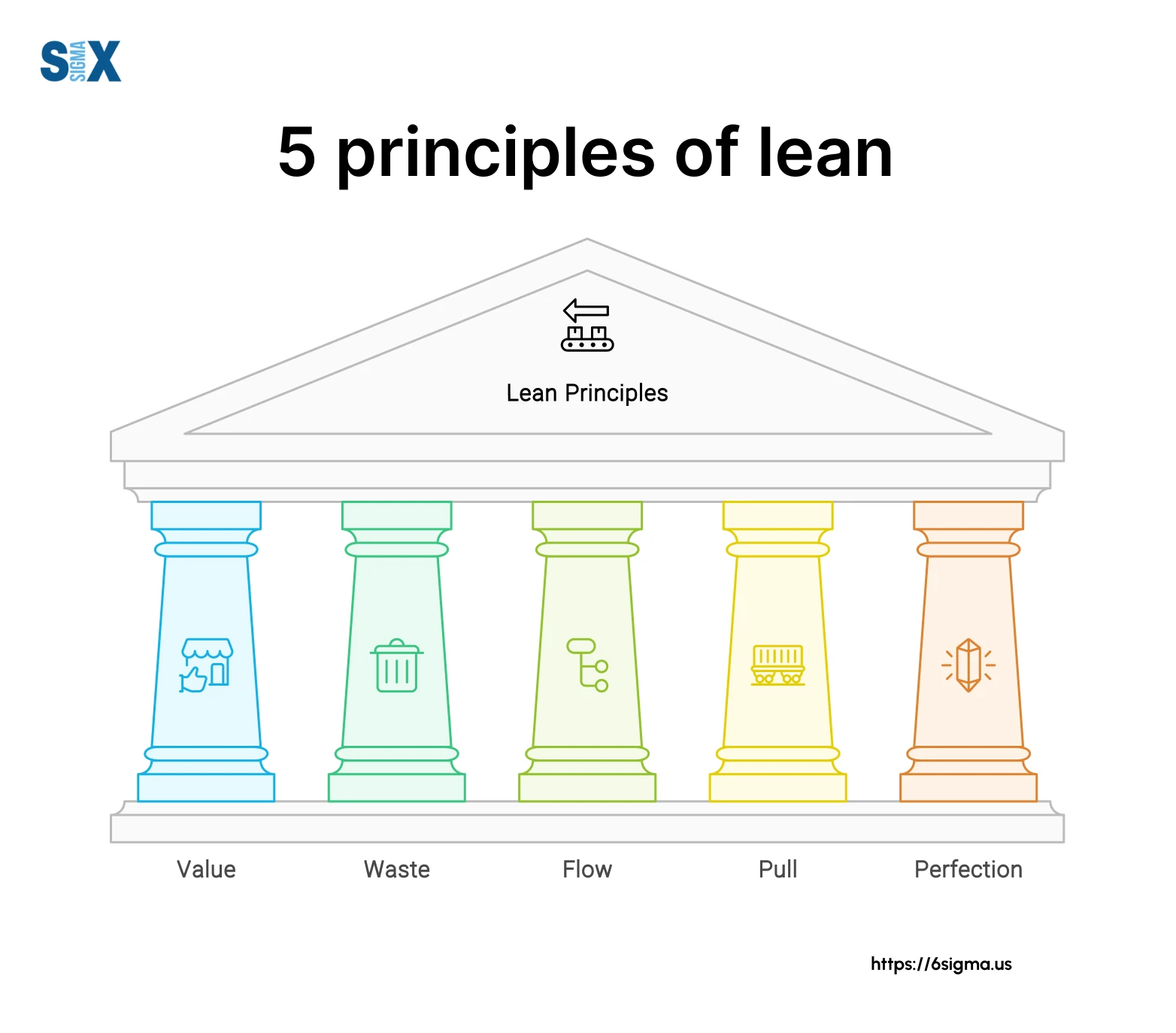
Understanding How Lean Principles Impact Efficiency
At its core, lean principles are about doing more with less. This means minimizing waste in all its forms – from excess inventory to unnecessary motion and defects. The eight wastes, often remembered by the acronym “DOWNTIME” (Defects, Overproduction, Waiting, Non-Utilized Talent, Transportation, Inventory, Motion, Extra-Processing), serve as a roadmap for identifying areas where resources are being squandered.
By systematically addressing these wastes, manufacturers can create a smoother, more efficient workflow. For example, reducing inventory levels minimizes storage costs and the risk of obsolescence. Streamlining transportation routes saves time and fuel. Eliminating defects improves product quality and reduces rework. All these changes contribute to a more profitable and sustainable operation. To succeed, businesses must foster a culture of continuous improvement, where employees are empowered to identify and solve problems at every level. This iterative process leads to sustained gains over time.
Another key component is standardizing processes. When tasks are performed consistently, there is less room for error and variation. Standard work instructions provide clear guidelines for employees, ensuring that everyone is on the same page and that best practices are followed. This not only improves efficiency but also makes it easier to train new employees and maintain quality standards.
Examining How Lean Principles Minimize Waste
Waste in manufacturing can take many forms, often hidden within complex processes. Lean principles offer a systematic approach to uncovering and eliminating these inefficiencies. Overproduction, producing more than what is needed, is a major source of waste. It leads to excess inventory, which ties up capital and requires additional storage space.
Waiting, whether it’s for materials, equipment, or information, disrupts the flow of production and reduces throughput. Transportation, moving materials unnecessarily, adds cost and increases the risk of damage. Non-utilized talent, failing to leverage the skills and knowledge of employees, represents a significant loss of potential.
Defects, producing faulty products, result in rework, scrap, and customer dissatisfaction. Inventory, holding excessive amounts of raw materials, work-in-progress, or finished goods, ties up capital and increases storage costs. Motion, unnecessary movement of people or equipment, wastes time and energy. Extra-processing, performing unnecessary steps in the manufacturing process, adds cost and doesn’t add value.
By systematically identifying and addressing each of these wastes, manufacturers can significantly improve their operational efficiency. Value stream mapping is a powerful tool for visualizing the entire manufacturing process, from raw materials to finished goods. This allows businesses to identify bottlenecks and areas where waste is occurring.
Investigating How Lean Principles Improve Productivity
Improved productivity is a direct result of implementing lean principles. By eliminating waste, standardizing processes, and empowering employees, manufacturers can achieve significant gains in output. One-piece flow, moving products through the manufacturing process one unit at a time, minimizes work-in-progress inventory and reduces lead times. This allows businesses to respond more quickly to customer demand and improve customer satisfaction.
Pull systems, where production is triggered by customer demand, prevent overproduction and ensure that resources are only used when needed. This reduces inventory levels and improves cash flow. Kanban systems, visual signaling systems, are often used to manage pull systems and ensure that materials are available when needed.
Another crucial aspect of improving productivity is investing in employee training and development. When employees have the skills and knowledge they need to perform their jobs effectively, they are more productive and less likely to make mistakes. Empowering employees to identify and solve problems also leads to continuous improvement and increased efficiency.
For example, imagine a factory producing widgets. Before implementing lean principles, the factory might have a large backlog of orders, long lead times, and significant amounts of waste. After implementing lean principles, the factory could see a significant reduction in lead times, a decrease in inventory levels, and a boost in productivity. The resulting improvements could be measured with key performance indicators, such as overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) and first-pass yield.
Furthermore, the use of technology can greatly improve productivity under lean principles. Utilizing the Cloud for data and communications can improve the flow of information, even enabling larger file transfers such as multiple files each in the gb size range.
Applying How Lean Principles Benefit The Overall Process
The benefits of implementing lean principles extend beyond just improved efficiency and productivity. A lean manufacturing environment is also a safer and more sustainable environment. By reducing waste and minimizing the use of resources, manufacturers can reduce their environmental impact.
Improved safety is another key benefit. By standardizing processes and eliminating unnecessary motion, manufacturers can reduce the risk of accidents and injuries. A clean and organized workspace, often achieved through the 5S methodology (Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize, Sustain), also contributes to a safer work environment.
Furthermore, lean principles foster a culture of continuous improvement and collaboration. When employees are empowered to identify and solve problems, they become more engaged and motivated. This leads to higher levels of job satisfaction and a more positive work environment. By focusing on customer needs and eliminating waste, manufacturers can create a more value-driven organization that is better positioned for long-term success.




